Several cases of unusual thrombotic events and thrombocytopenia have developed after vaccination with the recombinant adenoviral vector encoding the spike protein antigen of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (ChAdOx1 nCov-19, AstraZeneca). More data were needed on the pathogenesis of this unusual clotting disorder.
We assessed the clinical and laboratory features of 11 patients in Germany and Austria in whom thrombosis or thrombocytopenia had developed after vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCov-19. We used a standard enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect platelet factor 4 (PF4)-heparin antibodies and a modified (PF4-enhanced) platelet-activation test to detect platelet-activating antibodies under various reaction conditions. Included in this testing were samples from patients who had blood samples referred for investigation of vaccine-associated thrombotic events, with 28 testing positive on a screening PF4-heparin immunoassay.
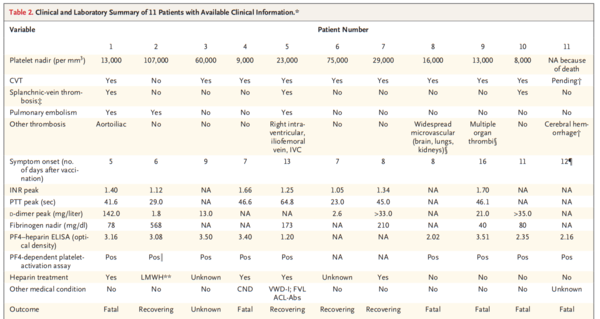
Of the 11 original patients, 9 were women, with a median age of 36 years (range, 22 to 49). Beginning 5 to 16 days after vaccination, the patients presented with one or more thrombotic events, with the exception of 1 patient, who presented with fatal intracranial hemorrhage. Of the patients with one or more thrombotic events, 9 had cerebral venous thrombosis, 3 had splanchnic-vein thrombosis, 3 had pulmonary embolism, and 4 had other thromboses; of these patients, 6 died. Five patients had disseminated intravascular coagulation. None of the patients had received heparin before symptom onset. All 28 patients who tested positive for antibodies against PF4-heparin tested positive on the platelet-activation assay in the presence of PF4 independent of heparin. Platelet activation was inhibited by high levels of heparin, Fc receptor-blocking monoclonal antibody, and immune globulin (10 mg per milliliter). Additional studies with PF4 or PF4-heparin affinity purified antibodies in 2 patients confirmed PF4-dependent platelet activation.
Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCov-19 can result in the rare development of immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia mediated by platelet-activating antibodies against PF4, which clinically mimics autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
SARS-CoV-2のスパイクタンパク抗原をコードする組換えアデノウイルスベクター(ChAdOx1 nCov-19、AstraZeneca社)を用いたワクチン接種後に、異常な血栓現象と血小板減少症を発症した症例が数例ある。この珍しい血液凝固障害の病態について,さらなるデータが必要であった。
ドイツとオーストリアで、ChAdOx1 nCov-19のワクチン接種後に血栓症または血小板減少症を発症した11人の患者の臨床的および実験的特徴を評価した。血小板第4因子(PF4)-ヘパリン抗体を検出するための標準的な酵素結合免疫吸着法と、血小板活性化抗体を検出するための改良型(PF4強化型)血小板活性化試験を様々な反応条件で行った。この検査には,ワクチンに関連した血栓症の調査のために血液を採取した患者の検体が含まれており,スクリーニング用のPF4-ヘパリン免疫測定法で28例が陽性となった。
初診患者11名のうち、9名が女性で、年齢中央値は36歳(範囲、22~49歳)であった。ワクチン接種の5~16日後から,1名を除く患者に1つ以上の血栓イベントが発生し,致命的な頭蓋内出血が認められた。1つ以上の血栓症を呈した患者のうち,9名が脳静脈血栓症,3名が脾静脈血栓症,3名が肺塞栓症,4名がその他の血栓症であり,このうち6名が死亡した.5人の患者が播種性血管内凝固症候群に罹患していた。症状が出る前にヘパリンを投与されていた患者はいなかった。PF4-ヘパリンに対する抗体が陽性であった28名の患者全員が,ヘパリンとは独立したPF4の存在下での血小板活性化アッセイに陽性であった.血小板活性化は,高濃度のヘパリン,Fc受容体遮断モノクローナル抗体,免疫グロブリン(10mg/ml)によって抑制された。2名の患者において、PF4またはPF4-ヘパリン親和性精製抗体を用いた追加試験により、PF4依存性の血小板活性化が確認された。
ChAdOx1 nCov-19によるワクチン接種は,PF4に対する血小板活性化抗体を介する免疫性血小板減少症をまれに発症させる可能性があり,臨床的には自己免疫性ヘパリン誘発性血小板減少症を模倣している。
Figure1 Reactivity of Patient Serum on Platelet-Activation Assays and Immunoassays
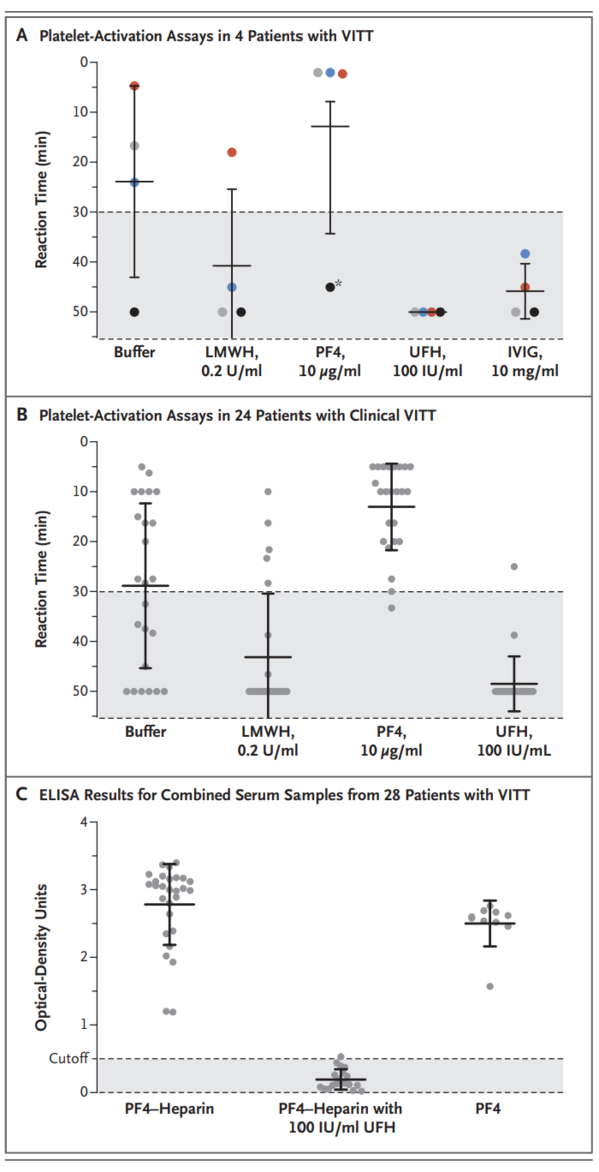
Table2 Clinical and Laboratory Summary of 11 Patients with Available Clinical Information
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2104840?articleTools=true