Evidence is lacking about any additional benefits of introducing remdesivir on top of dexamethasone, and the optimal timing of initiation.
In a territory-wide cohort of 10,445 COVID-19 patients from Hong Kong who were hospitalized between 21st January 2020 and 31st January 2021, 1544 patients had received dexamethasone during hospitalization. Exposure group consisted of patients who had initiated remdesivir prior to dexamethasone (n=93), or co-initiated the two drugs simultaneously (n=373); whereas non-exposure group included patients who were given remdesivir after dexamethasone (n=149), or those without remdesivir use (n=929). Multiple imputation and inverse probability of treatment weighting for propensity score were applied and hazard ratios (HR) of event outcomes were estimated using Cox regression models.
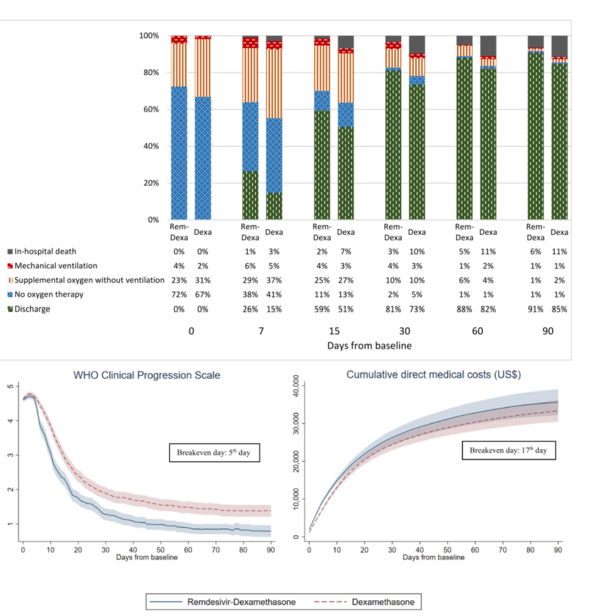
Time to clinical improvement (HR=1.23, 95%CI 1.02-1.49, p=0.032) and positive IgG antibody (HR=1.22, 95%CI 1.02-1.46, p=0.029) were significantly shorter in the exposure group than that of non-exposure. The exposure group had a shorter hospital length of stay by 2.65 days among survivors, lower WHO clinical progression scale scores from five days of follow-up onwards, lower risks of in-hospital death (HR=0.59, 95%CI 0.36-0.98, p=0.042) and composite outcomes; and without experiencing an increased risk of ARDS. Differences in the cumulative direct medical costs between groups were no longer significant from 17 days of follow-up onwards.
Initiation of remdesivir prior to or simultaneously with dexamethasone was associated with significantly shorter time to clinical improvement and positive IgG antibody, lower risk of in-hospital death, in addition to shorter length of hospital stay in patients with moderate COVID-19.
デキサメタゾンに加えてレムデシビルを導入することで得られる追加効果や、最適な導入時期についてのエビデンスは不足している。
2020年1月21日から2021年1月31日の間に入院した香港のCOVID-19患者10,445人の地域全体のコホートにおいて、1544人の患者が入院中にデキサメサゾンを投与されていた。暴露群は、デキサメタゾンの前にレムデシビルを投与開始した患者(n=93)、または2剤を同時に投与開始した患者(n=373)であり、非暴露群は、デキサメタゾンの後にレムデシビルを投与された患者(n=149)、またはレムデシビルを使用していない患者(n=929)であった。傾向スコアに多重帰属と治療の逆確率の重み付けを適用し、Cox回帰モデルを用いてイベントアウトカムのハザード比(HR)を推定した。
臨床症状の改善までの期間(HR=1.23, 95%CI 1.02-1.49, p=0.032)およびIgG抗体陽性までの期間(HR=1.22, 95%CI 1.02-1.46, p=0.029)は、曝露群の方が非曝露群よりも有意に短かった。曝露群では、生存者の在院日数が2.65日短縮され、5日目以降のWHO clinical progression scaleスコアが低下し、院内死亡(HR=0.59、95%CI 0.36-0.98、p=0.042)および複合転帰のリスクが低下し、ARDSのリスク上昇を経験せずに済んだ。累積直接医療費のグループ間の差は、追跡期間17日目以降はもはや有意ではなかった。
中等症のCOVID-19患者において、レムデシビルをデキサメタゾンに先行して、または同時に投与を開始することは、臨床症状の改善とIgG抗体の陽性化までの期間を有意に短縮し、院内死亡のリスクを低下させ、さらに入院期間を短縮することと関連していた。
Figure 1
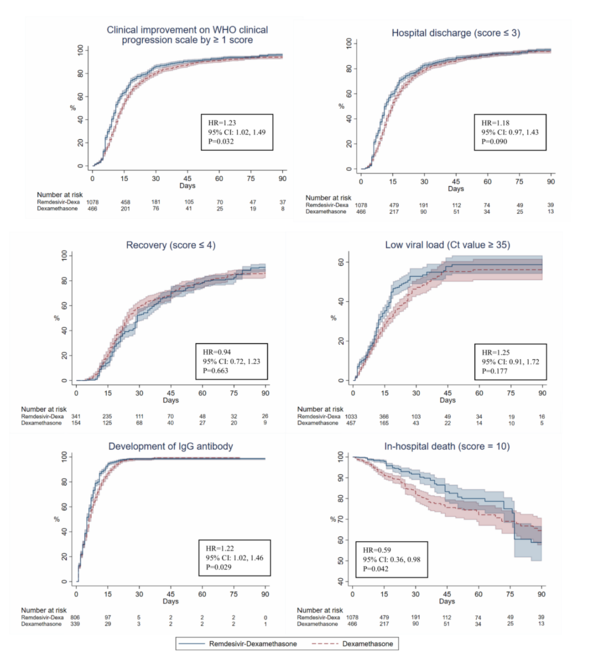
Figure 2
https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab728/6356217