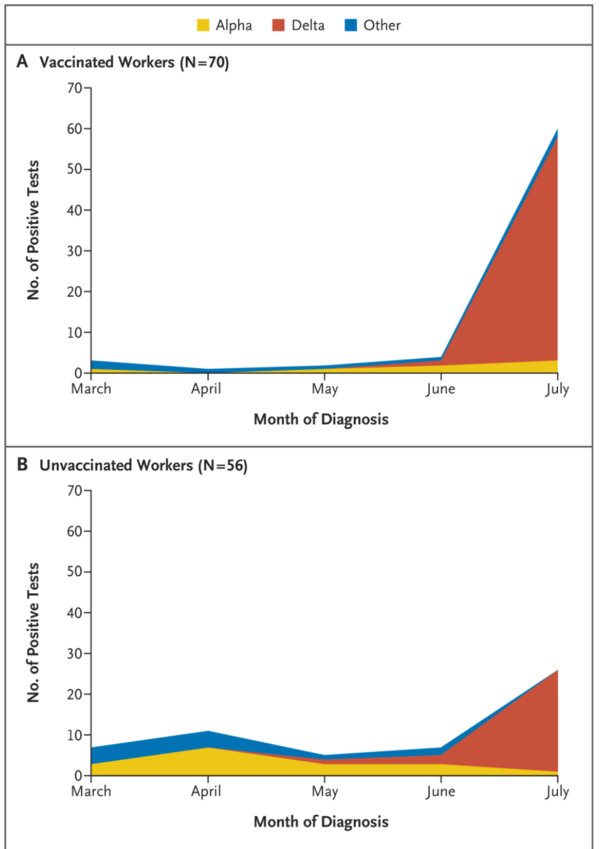
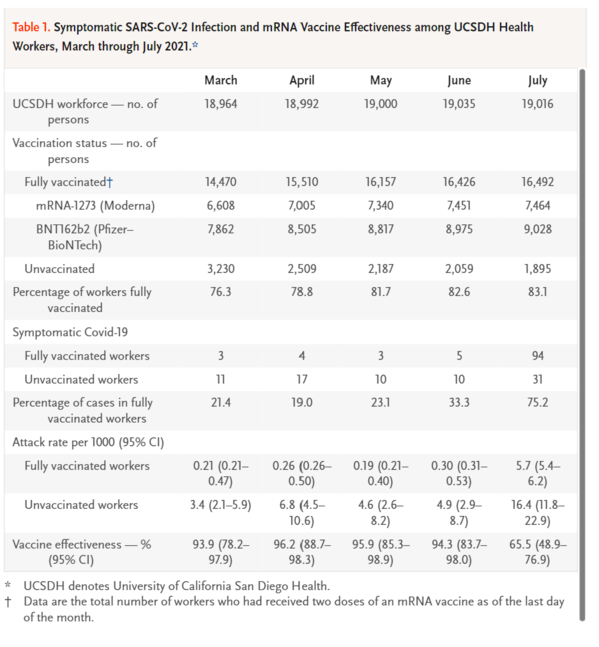
In December 2020, the University of California San Diego Health (UCSDH) workforce experienced a dramatic increase in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. Vaccination with mRNA vaccines began in mid-December 2020; by March, 76% of the workforce had been fully vaccinated, and by July, the percentage had risen to 83%. Infections had decreased dramatically by early February 2021.1 Between March and June, fewer than 30 health care workers tested positive each month. However, coincident with the end of California's mask mandate on June 15 and the rapid dominance of the B.1.617.2 (delta) variant that first emerged in mid-April and accounted for over 95% of UCSDH isolates by the end of July (Figure 1), infections increased rapidly, including cases among fully vaccinated persons.
(Omission)
Vaccine effectiveness exceeded 90% from March through June but fell to 65.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 48.9 to 76.9) in July (Table 1).
(Omission)
The dramatic change in vaccine effectiveness from June to July is likely to be due to both the emergence of the delta variant and waning immunity over time, compounded by the end of masking requirements in California and the resulting greater risk of exposure in the community. Our findings underline the importance of rapidly reinstating nonpharmaceutical interventions, such as indoor masking and intensive testing strategies, in addition to continued efforts to increase vaccinations, as strategies to prevent avoidable illness and deaths and to avoid mass disruptions to society during the spread of this formidable variant. Furthermore, if our findings on waning immunity are verified in other settings, booster doses may be indicated.
2020年12月、カリフォルニア サンディエゴ ヘルス大学(UCSDH)の職員は、SARS-CoV-2感染症の劇的な増加を経験した。2020年12月中旬にmRNAワクチンの接種を開始し、3月までに職員の76%が完全に接種を完了し、7月にはその割合が83%にまで上昇した。2021年2月初旬には、感染が劇的に減少した。3月から6月にかけて、毎月30人未満の医療従事者が陽性と判定された。しかし、6月15日にカリフォルニア州のマスク着用義務が終了したことや、4月中旬に出現し、7月末までにUCSDHの分離株の95%以上を占めたB.1.617.2(delta)変異体が急速に優勢になったことに伴い(図1)、完全にワクチンを接種した人の症例も含めて、感染が急速に増加した。
(中略)
ワクチンの有効性は、3月から6月までは90%を超えていたが、7月には65.5%(95%信頼区間[CI]、48.9~76.9)に低下した(表1)。
(中略)
6月から7月にかけてワクチンの効果が劇的に変化したのは、デルタ変異株の出現と、時間の経過に伴う免疫の低下の両方が原因であると考えられ、さらにカリフォルニア州ではマスク着用の義務が終了し、その結果、地域社会での曝露のリスクが高まったことも影響していると思われる。今回の結果は、回避可能な病気や死亡を防ぎ、この恐ろしい変異株が蔓延して社会が大混乱に陥るのを避けるための戦略として、ワクチン接種を増やす努力を続けることに加えて、屋内でのマスク着用や集中的な検査戦略などの非医薬品的な介入を迅速に再開することの重要性を強調するものである。さらに、免疫の低下に関する今回の調査結果が他の環境でも検証されれば、ブースター投与が必要になる可能性がある。
https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMc2112981