(Excerpt)
One measure of viral spread is the R0, the expected number of secondary infectious cases produced by a primary infectious case. This calculation is used to determine the potential for epidemic spread in a susceptible population. The effective reproduction number, Rt, determines the potential for epidemic spread at a specific time t under the control measures in place (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Concepts of the Effective Reproduction Number
The effective reproduction number (Rt) of a viral infection is the mean number of additional infections caused by an initial infection in a population at a specific time.
Figure 2. The Effective Reproduction Number (Rt) Estimates Based on Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases in Wuhan, China
The effective reproduction number Rt is defined as the mean number of secondary cases generated by a typical primary case at time t in a population, calculated for the whole period over a 5-day moving average. Results are shown since January 1, 2020, given the limited number of diagnosed cases and limited diagnosis capacity in December 2019. The darkened horizontal line indicates Rt = 1, below which sustained transmission is unlikely so long as antitransmission measures are sustained, indicating that the outbreak is under control. (Pan A. JAMA. Published online April 10, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6130)
In early through mid-January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in Wuhan had an Rt of 3 to 4. In other words, each case spread to an average of 3 to 4 others. That is a striking number: compare it to the Rt of 1.4 to 1.7 for influenza, which is a disease that spreads widely around the world every year. Couple that with the fact that each new generation of SARS-CoV-2 cases occurs every 5 days, and it is clear to see how this epidemic was spreading out of control.
公衆衛生対策とSARS-CoV-2の再生産数 (JAMA 2020.05.01)
(抜粋)
ウイルスの蔓延の指標の一つとして、一次感染例によって生み出される二次感染例の予想数である基本再生産数R0がある。この計算は、罹患する可能性のある集団における伝染性伝播の可能性を決定するために使用される。効果的再生産数Rtは、実施されている制御手段の下で、特定の時間tにおける流行拡大の可能性を示す数である(図1)。
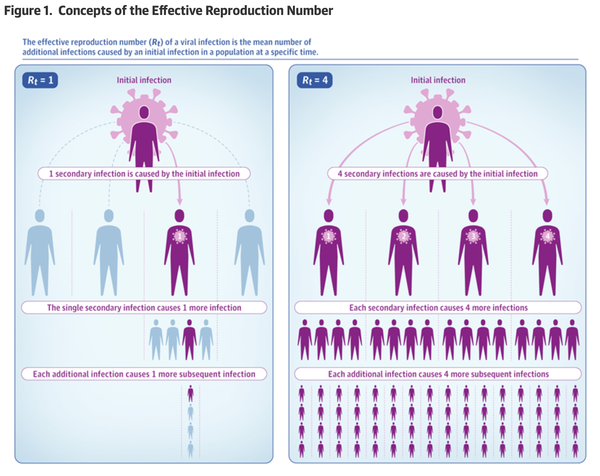
図1. 効果的再生産数Rtの概念 ウイルス感染の効果的再生産数(Rt)は、特定の時間に集団内で初期感染によって引き起こされた2次感染者数の平均である。
(出典 jamanetwork.com)
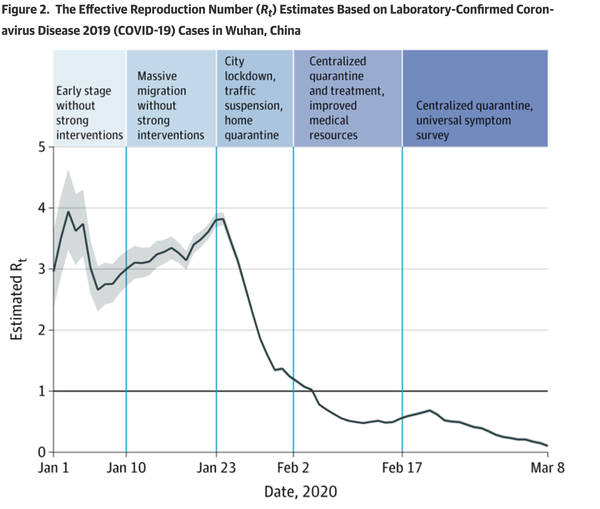
図2. 中国・武漢での実験室確認済み新型コロナウィルス感染症(COVID-19)症例に基づく有効生殖数(Rt)の推定値
(出典 jamanetwork.com)
有効再生産数Rtは、母集団における時刻tにおける代表的な一次症例から発生した二次症例の平均数として定義され、5日移動平均で全期間にわたって算出される。2019年12月の鑑定診断症例数と検査による診断能力が限られていたことを考慮して、2020年1月1日以降の結果を示しています。暗くなっている横線はRt=1を示しており、これ以下では感染対策が持続する限り持続的な感染は考えられず、アウトブレイクが制御されていることを示している。(Pan A. JAMA. Published online April 10, 2020. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6130)
2020 年 1 月初旬から中旬にかけての武漢での SARS-CoV-2 の流行は、Rt が 3~4 であった。 言い換えれば、各症例は平均して 3~4 人の他の症例に伝播したことになる。これは驚くべき数字であり、毎年世界中で流行しているインフルエンザのRt1.4~1.7と比較してみてほしい。SARS-CoV-2の新たな感染者が5日ごとに発生しているという事実と組み合わせて考えると、この流行がどれだけ制御不能に広がっていたかがよくわかる。
(千葉大学大学院医学研究院 救急集中治療医学 中田孝明 コメント)
Reproduction Number (Rt)のコンセプト(図1)と具体例(図2)が示されており、Reproduction Numberを理解するのに良い論文。ご興味あれば原文をご確認ください。
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2765665
日本/米国のCOVID-19のReproduction Numberのサイトは下記です。
https://rt-live-japan.com/
https://rt.live