Severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is associated with dysregulated inflammation. The effects of combination treatment with baricitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, plus remdesivir are not known.
We conducted a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial evaluating baricitinib plus remdesivir in hospitalized adults with Covid-19. All the patients received remdesivir (≤10 days) and either baricitinib (≤14 days) or placebo (control). The primary outcome was the time to recovery. The key secondary outcome was clinical status at day 15.
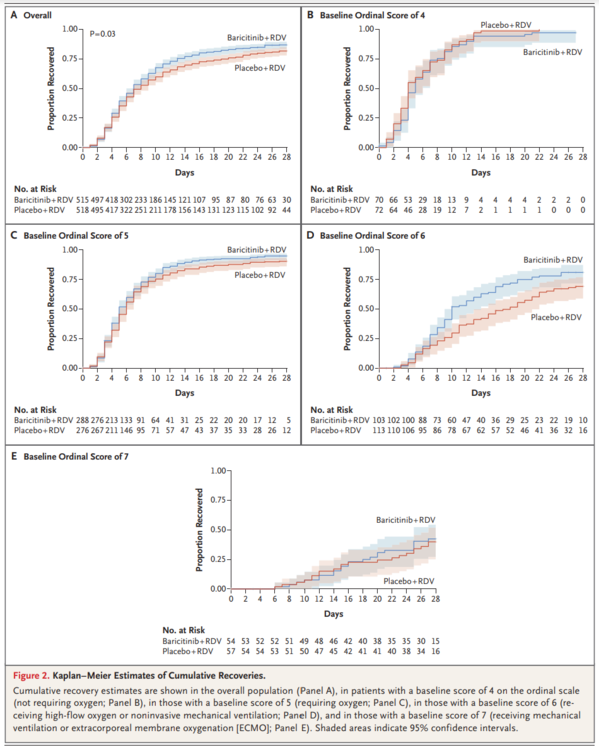
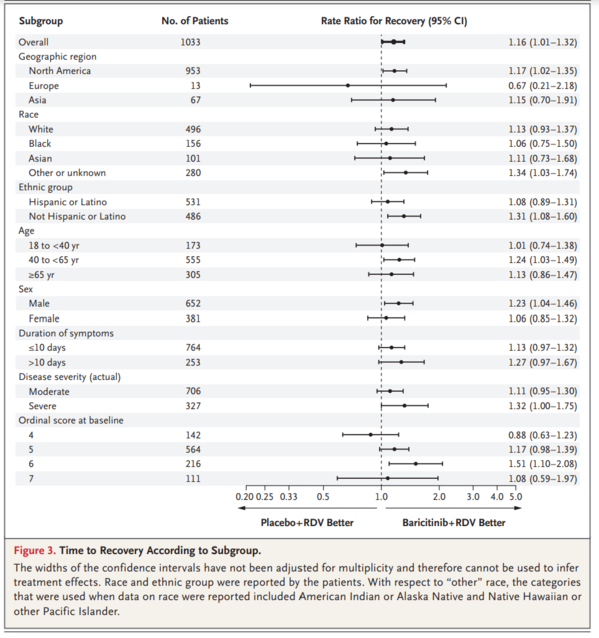
A total of 1033 patients underwent randomization (with 515 assigned to combination treatment and 518 to control). Patients receiving baricitinib had a median time to recovery of 7 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 6 to 8), as compared with 8 days (95% CI, 7 to 9) with control (rate ratio for recovery, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.32; P=0.03), and a 30% higher odds of improvement in clinical status at day 15 (odds ratio, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 1.6). Patients receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation at enrollment had a time to recovery of 10 days with combination treatment and 18 days with control (rate ratio for recovery, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.10 to 2.08). The 28-day mortality was 5.1% in the combination group and 7.8% in the control group (hazard ratio for death, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.39 to 1.09). Serious adverse events were less frequent in the combination group than in the control group (16.0% vs. 21.0%; difference, −5.0 percentage points; 95% CI, −9.8 to −0.3; P=0.03), as were new infections (5.9% vs. 11.2%; difference, −5.3 percentage points; 95% CI, −8.7 to −1.9; P=0.003).
Baricitinib plus remdesivir was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time and accelerating improvement in clinical status among patients with Covid-19, notably among those receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation. The combination was associated with fewer serious adverse events.
Covid-19は、炎症の調節障害と関連している。Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitorであるバリシチニブとレムデシビルの併用療法の効果は不明である。
Covid-19 で入院した成人を対象に,バリシチニブとレムデシビルの併用を評価する二重盲検,無作為化,プラセボ対照試験を実施した.全患者にレムデシビル(10日以内)と、バリシチニブ(14日以内)またはプラセボ(対照)を投与した。主要アウトカムは回復までの時間であった。主要な副次的転帰は15日目の臨床状態であった。
合計 1033 例の患者が無作為化を受けた(うち 515 例が併用療法、518 例が対照群)。バリシチニブを投与された患者の回復までの期間の中央値は7日(95%信頼区間[CI]、6~8日)であったのに対し、対照群では8日(95%CI、7~9日)であり(回復率比、1.16;95%CI、1.01~1.32;P=0.03)、15日目の臨床状態の改善のオッズは30%高かった(オッズ比、1.3;95%CI、1.0~1.6)。登録時に高流量酸素または非侵襲的人工呼吸を受けた患者の回復までの期間は,併用療法で10日,対照群で18日であった(回復率比,1.51;95%CI,1.10~2.08)。28 日間の死亡率は併用群で 5.1%、対照群で 7.8%であった(死亡のハザード比、0.65;95%CI、0.39~1.09)。重篤な有害事象の発生頻度は対照群よりも併用群の方が低かった(16.0%対21.0%、差は-5.0%ポイント、95%CI、-9.8~-0.3、P=0.03)が、新規感染症(5.9%対11.2%、差は-5.3%ポイント、95%CI、-8.7~-1.9、P=0.003)。
バリシチニブとレムデシビルの併用は、特に高流量酸素または非侵襲的人工呼吸を受けている患者において、Covid-19患者の回復時間を短縮し、臨床状態の改善を促進する点でレムデシビル単独よりも優れていた。この併用療法は重篤な有害事象の発生を抑制した。
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2031994?articleTools=true