Recent data suggest that complications and death from coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) may be related to high viral loads.
In this ongoing, double-blind, phase 1-3 trial involving nonhospitalized patients with Covid-19, we investigated two fully human, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein, used in a combined cocktail (REGN-COV2) to reduce the risk of the emergence of treatment-resistant mutant virus. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive placebo, 2.4 g of REGN-COV2, or 8.0 g of REGN-COV2 and were prospectively characterized at baseline for endogenous immune response against SARS-CoV-2 (serum antibody-positive or serum antibody-negative). Key end points included the time-weighted average change from baseline in viral load from day 1 through day 7 and the percentage of patients with at least one Covid-19-related medically attended visit through day 29. Safety was assessed in all patients.
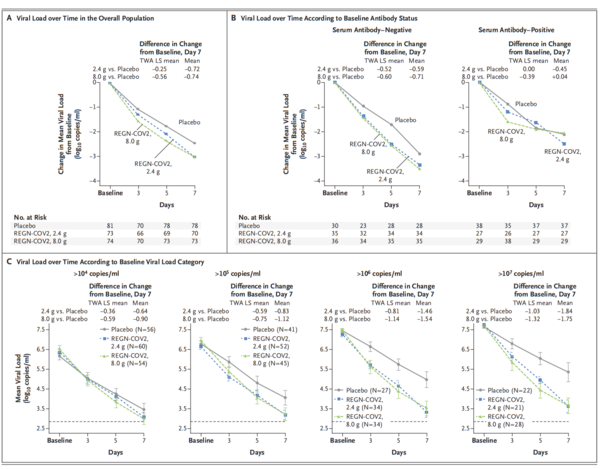
Data from 275 patients are reported. The least-squares mean difference (combined REGN-COV2 dose groups vs. placebo group) in the time-weighted average change in viral load from day 1 through day 7 was −0.56 log10 copies per milliliter (95% confidence interval [CI], −1.02 to −0.11) among patients who were serum antibody-negative at baseline and −0.41 log10 copies per milliliter (95% CI, −0.71 to −0.10) in the overall trial population. In the overall trial population, 6% of the patients in the placebo group and 3% of the patients in the combined REGN-COV2 dose groups reported at least one medically attended visit; among patients who were serum antibody-negative at baseline, the corresponding percentages were 15% and 6% (difference, −9 percentage points; 95% CI, −29 to 11). The percentages of patients with hypersensitivity reactions, infusion-related reactions, and other adverse events were similar in the combined REGN-COV2 dose groups and the placebo group.
In this interim analysis, the REGN-COV2 antibody cocktail reduced viral load, with a greater effect in patients whose immune response had not yet been initiated or who had a high viral load at baseline. Safety outcomes were similar in the combined REGN-COV2 dose groups and the placebo group.
最近のデータでは、Covid-19の合併症や死亡が高ウイルス量と関連している可能性が示唆されている。
Covid-19 の非入院患者を対象とした進行中の二重盲検第 1~3 相試験では、SARS-CoV-2スパイクタンパクに対する 2 種類の完全ヒト中和モノクローナル抗体を,治療抵抗性の突然変異ウイルスの出現リスクを低減するために混合薬(REGN-COV2)として使用した。患者はプラセボ、2.4gのREGN-COV2、または8.0gのREGN-COV2に無作為に割り付けられ、ベースラインでSARS-CoV-2に対する内因性免疫反応(血清抗体陽性または血清抗体陰性)をプロスペクティブに評価された。主要エンドポイントは、1日目から7日目までのウイルス量のベースラインからの時間加重平均変化、および29日目までに少なくとも1回のCovid-19関連の通院をした患者の割合であった。安全性は全患者で評価された。
275 例の患者からのデータが報告されている。1日目から7日目までのウイルス量の時間加重平均変化量の最小二乗平均差(REGN-COV2併用群とプラセボ群)は、ベースライン時に血清抗体陰性であった患者では-0.56 log10 copies per milliliter(95%信頼区間[CI]、-1.02~-0.11)であり、試験集団全体では-0.41 log10 copies per milliliter(95%CI、-0.71~-0.10)であった。試験全体では、プラセボ群では6%、REGN-COV2併用群では3%の患者が少なくとも1回の診察を受けたと報告した;ベースライン時に血清抗体陰性であった患者の対応する割合は15%と6%であった(差は-9%ポイント、95%CI、-29~11)。過敏症反応、輸液関連反応、およびその他の有害事象を起こした患者の割合は、REGN-COV2併用投与群とプラセボ群で同程度であった。
この中間解析では、REGN-COV2抗体カクテルはウイルス量を低下させ、免疫反応がまだ開始されていない患者やベースライン時のウイルス量が高い患者でより大きな効果を示した。安全性の転帰は、REGN-COV2併用投与群とプラセボ群で同様であった。
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2035002?articleTools=true