The efficacy of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is unclear.
We evaluated tocilizumab and sarilumab in an ongoing international, multifactorial, adaptive platform trial. Adult patients with Covid-19, within 24 hours after starting organ support in the intensive care unit (ICU), were randomly assigned to receive tocilizumab (8 mg per kilogram of body weight), sarilumab (400 mg), or standard care (control). The primary outcome was respiratory and cardiovascular organ support-free days, on an ordinal scale combining in-hospital death (assigned a value of −1) and days free of organ support to day 21. The trial uses a Bayesian statistical model with predefined criteria for superiority, efficacy, equivalence, or futility. An odds ratio greater than 1 represented improved survival, more organ support-free days, or both.
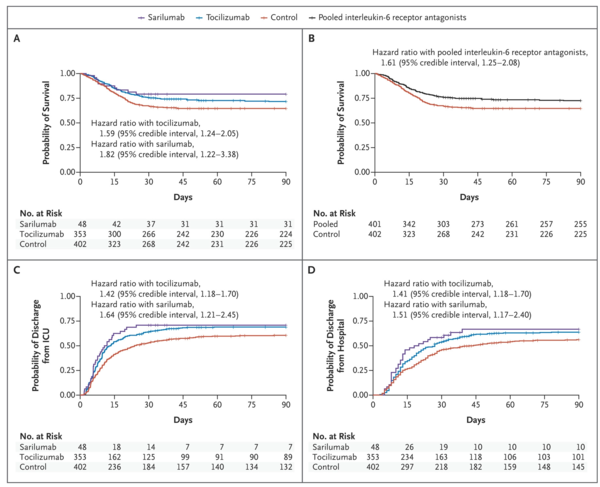
Both tocilizumab and sarilumab met the predefined criteria for efficacy. At that time, 353 patients had been assigned to tocilizumab, 48 to sarilumab, and 402 to control. The median number of organ support-free days was 10 (interquartile range, −1 to 16) in the tocilizumab group, 11 (interquartile range, 0 to 16) in the sarilumab group, and 0 (interquartile range, −1 to 15) in the control group. The median adjusted cumulative odds ratios were 1.64 (95% credible interval, 1.25 to 2.14) for tocilizumab and 1.76 (95% credible interval, 1.17 to 2.91) for sarilumab as compared with control, yielding posterior probabilities of superiority to control of more than 99.9% and of 99.5%, respectively. An analysis of 90-day survival showed improved survival in the pooled interleukin-6 receptor antagonist groups, yielding a hazard ratio for the comparison with the control group of 1.61 (95% credible interval, 1.25 to 2.08) and a posterior probability of superiority of more than 99.9%. All secondary analyses supported efficacy of these interleukin-6 receptor antagonists.
In critically ill patients with Covid-19 receiving organ support in ICUs, treatment with the interleukin-6 receptor antagonists tocilizumab and sarilumab improved outcomes, including survival.
COVID-19の重症患者に対するインターロイキン-6受容体拮抗薬の有効性は不明である。
我々は、現在進行中の国際的な多因子適応プラットフォーム試験において、トシリズマブとサリルマブを評価した。集中治療室(ICU)で臓器支持を開始してから24時間以内のCOVID-19の成人患者を対象に、トシリズマブ(体重1kgあたり8mg)、サリルズマブ(400mg)、標準治療(コントロール)のいずれかに無作為に割り付けた。主要アウトカムは、院内死亡(-1の値が割り当てられた)と21日目までの臓器支持を受けていない日数を組み合わせた順序尺度で、呼吸器および心血管系の臓器支持を受けていない日数であった。この試験では、優越性、有効性、同等性、または無益性の事前に定義された基準を持つベイズ統計モデルを使用している。オッズ比が1より大きい場合は、生存率の改善、臓器支持なし日数の増加、またはその両方を表した。
トシリズマブとサリルズマブはいずれも事前に定義された有効性の基準を満たしていた。この時点で353人の患者がトシリズマブ、48人がサリルズマブ、402人が対照群に割り付けられていた。臓器支持がなかった日数の中央値は、トシリズマブ群で10日(四分位間値範囲、-1~16日)、サリルマブ群で11日(四分位間値範囲、0~16日)、対照群で0日(四分位間値範囲、-1~15日)であった。修正累積オッズ比の中央値は、対照群と比較してトシリズマブ群で1.64(95%信頼区間、1.25~2.14)、サリルズマブ群で1.76(95%信頼区間、1.17~2.91)であり、対照群に対する優越性の事後確率はそれぞれ99.9%以上、99.5%であった。90 日生存期間の解析では、プールされたインターロイキン-6 受容体拮抗薬群で生存期間の改善が示され、対照群と比較した場合のハザード比は 1.61(95%信頼区間、1.25~2.08)、99.9%以上の優越性の事後確率が得られました。すべての二次解析において、これらのインターロイキン-6受容体拮抗薬の有効性が支持された。
ICUで臓器支持を受けているCOVID-19の重症患者において、インターロイキン-6受容体拮抗薬であるトシリズマブとサリルズマブを投与したところ、生存期間を含む転帰が改善した。
Figure2 臓器支持のない日の分布
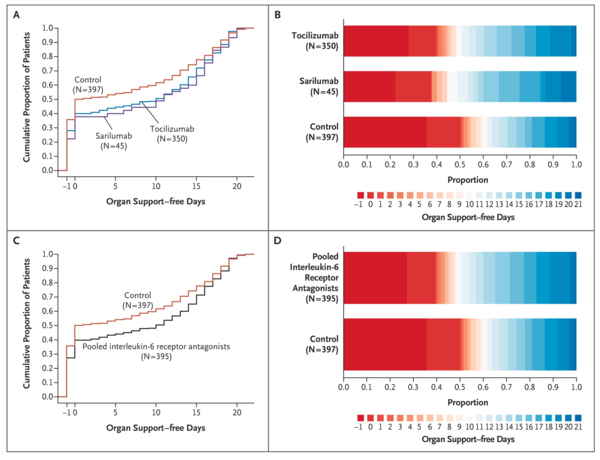
Figure3 Time-to-event解析
https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2100433