As mass vaccination campaigns against coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) commence worldwide, vaccine effectiveness needs to be assessed for a range of outcomes across diverse populations in a noncontrolled setting. In this study, data from Israel's largest health care organization were used to evaluate the effectiveness of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
All persons who were newly vaccinated during the period from December 20, 2020, to February 1, 2021, were matched to unvaccinated controls in a 1:1 ratio according to demographic and clinical characteristics. Study outcomes included documented infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), symptomatic Covid-19, Covid-19-related hospitalization, severe illness, and death. We estimated vaccine effectiveness for each outcome as one minus the risk ratio, using the Kaplan-Meier estimator.
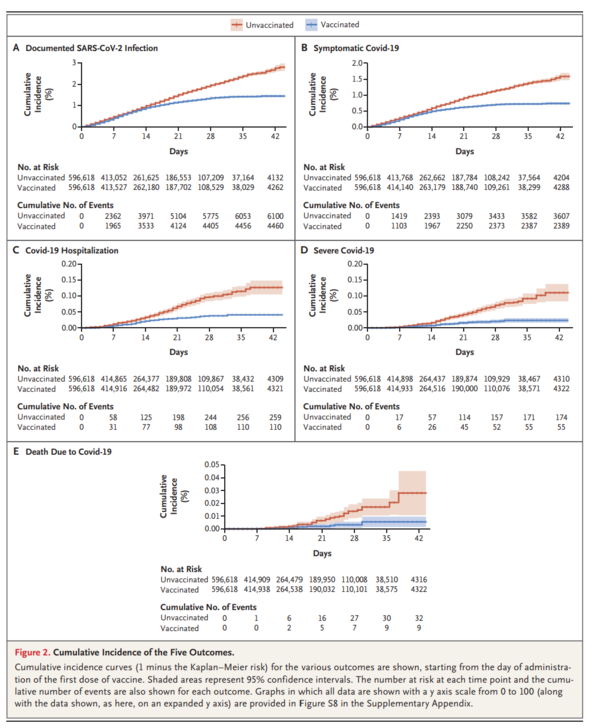
Each study group included 596,618 persons. Estimated vaccine effectiveness for the study outcomes at days 14 through 20 after the first dose and at 7 or more days after the second dose was as follows: for documented infection, 46% (95% confidence interval [CI], 40 to 51) and 92% (95% CI, 88 to 95); for symptomatic Covid-19, 57% (95% CI, 50 to 63) and 94% (95% CI, 87 to 98); for hospitalization, 74% (95% CI, 56 to 86) and 87% (95% CI, 55 to 100); and for severe disease, 62% (95% CI, 39 to 80) and 92% (95% CI, 75 to 100), respectively. Estimated effectiveness in preventing death from Covid-19 was 72% (95% CI, 19 to 100) for days 14 through 20 after the first dose. Estimated effectiveness in specific subpopulations assessed for documented infection and symptomatic Covid-19 was consistent across age groups, with potentially slightly lower effectiveness in persons with multiple coexisting conditions.
This study in a nationwide mass vaccination setting suggests that the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine is effective for a wide range of Covid-19-related outcomes, a finding consistent with that of the randomized trial.
COVID-19に対する大規模ワクチン接種運動が世界的に開始されるにあたり、ワクチンの有効性は、非対照の設定で多様な集団にわたる様々な転帰について評価する必要がある。本研究では、イスラエル最大の医療機関のデータを用いて、BNT162b2 mRNAワクチンの有効性を評価した。
2020 年 12 月 20 日から 2021 年 2 月 1 日までの期間に新規にワクチンを接種したすべての人を、人口統計学的および臨床的特徴に基づいて、ワクチンを接種していない対照者と 1:1 の比率でマッチングさせた。試験の転帰には、SARS-CoV-2への感染の診断、症候性COVID-19、COVID-19関連の入院、重症化、死亡が含まれた。Kaplan-Meier 推定法を用いて、各転帰についてワクチンの有効性をリスク比から 1 を引いた値として推定した。
各試験群には596,618人が含まれている。1回目の接種後14~20日目および2回目の接種後7日以上経過した時点での試験アウトカムに対するワクチン有効性の推定値は以下の通りであった。感染の診断については、46%(95%信頼区間[CI]、40~51)および92%(95%CI、88~95);症候性COVID-19については、57%(95%CI、50~63)および94%(95%CI、87~98);入院については、74%(95%CI、56~86)および87%(95%CI、55~100);重症化については、それぞれ62%(95%CI、39~80)および92%(95%CI、75~100)であった。COVID-19による死亡予防における推定有効性は、初回投与後14日目から20日目までの72%(95%CI、19~100)であった。感染の診断と症候性COVID-19について評価された特定のサブ集団における有効性の推定値は、年齢層を超えて一貫しており、複数の疾患を併存している人では有効性がわずかに低下する可能性があった。
この全国的な大規模接種環境での研究では、BNT162b2 mRNA ワクチンが幅広い範囲の COVID-19 関連の転帰に対して有効であることが示唆されており、無作為化試験の知見と一致している。
図:5つのアウトカムの累積発生率
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2101765?articleTools=true